Acid rain is a term used to describe rain
Acid rain is a term used to describe rain
by RM Shukla
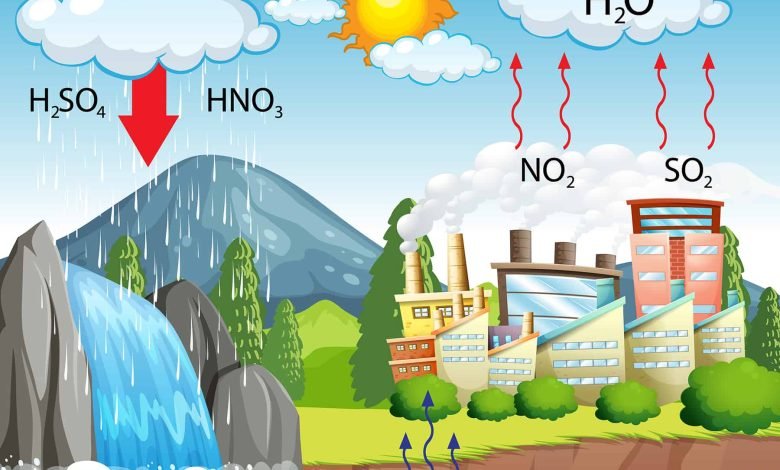
Acid rain is a term used to describe rain, snow, fog, or any form of precipitation that has been significantly polluted by sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), resulting in a lower pH level than normal rainwater. These pollutants are primarily released into the atmosphere through human activities such as burning fossil fuels, industrial emissions, and transportation. When these pollutants react with water vapor in the atmosphere, they form sulfuric acid and nitric acid, which then fall to the ground as acid rain.
Acid rain has detrimental effects on the environment. It can lead to the acidification of lakes, rivers, and streams, making them uninhabitable for aquatic life. The increased acidity can disrupt ecosystems, harm fish populations, and damage plant life. Acid rain can also erode buildings, monuments, and statues made of limestone or marble, as the acids react with the calcium carbonate present in these structures. Additionally, it can damage forests by leaching essential nutrients from the soil, causing nutrient imbalances and inhibiting the growth of trees.
Efforts have been made to reduce the impact of acid rain. Many countries have implemented regulations and pollution control measures to limit the emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from power plants, industries, and vehicles. The use of cleaner fuels, such as low-sulfur coal and alternative energy sources, has also been encouraged. International collaborations and agreements have played a significant role in addressing the issue of acid rain. While progress has been made, continued monitoring and mitigation efforts are necessary to protect the environment from the harmful effects of acid rain and ensure the sustainability of ecosystems for future generations










